Sign up to our newsletter
Receive news on the Alliance, upcoming events, and members activities in Sustainable Fashion


UNIDO is the specialized agency of the United Nations that promotes industrial development for poverty reduction, inclusive globalization and environmental sustainability. UNIDO’s mandate is to promote and accelerate inclusive and sustainable industrial development (ISID) in developing countries. UNIDO’s mandate is fully recognized in SDG-9, which calls to “Build resilient infrastructure, promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization and foster innovation”. Given the inter-linkages of the SDGs, the impact of ISID has both a direct and indirect effect, contributing towards the achievement of the 17 SDGs.
Accordingly, the Organization’s strategic priorities, contained in its current Medium Term Programme Framework, 2018-2021 is structured around its four strategic priorities of:
To support the development impact and effectiveness of its services, UNIDO applies a holistic and integrated programme framework that integrates the Organization’s four core functions in: (i) technical cooperation; (ii) analytical and research functions and policy advisory services; (iii) normative functions and standards and quality-related activities; and (iv) convening and partnerships for knowledge transfer, networking and industrial cooperation.
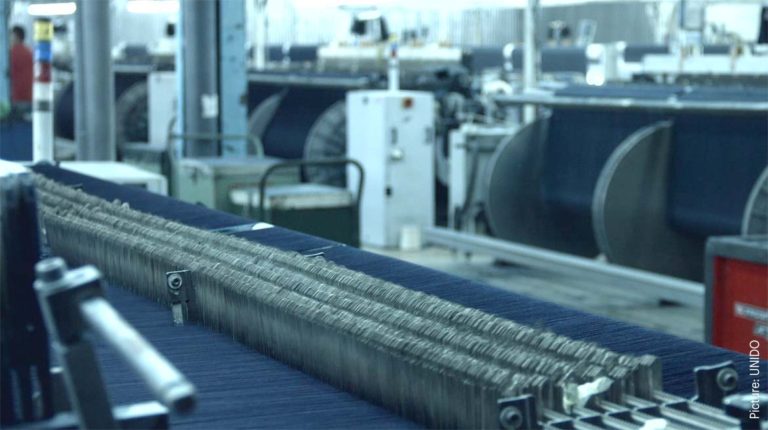


UNIDO’s Sustainable Fashion projects proposes a vision for a new fashion industry aligned with the principles of a circular economy and provides multiple benefits for business, society and the environment. Reducing industrial pollution and emissions is central to the Organization’s approach and contributes to improving health, tackling climate change, and supporting biodiversity. Furthermore, Sound Chemicals Management, Resource Efficient and Cleaner Production, and Circular Economy approaches contribute to broader efforts to improve sustainability performance at company level, as well as along the supply chain.
In creating capacities within industries, governments and institutions to meet their legal obligations under the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs), The Industrial Pollution Mitigation Division of the Department of Environment, contributes to a more sustainable fashion industry along the textiles, garment and leather supply chains. A wide range of activities from policy advice to technology transfer and pilot demonstration, support countries across the world to eliminate or reduce the release of harmful POPs into the environment. Several global and regional partnerships have been developed in this area, as well as intensive work in Africa, where UNIDO promotes Circular Economy in the Textile and Garment Sector through sustainable Chemicals and Wastes Management in Ethiopia and Lesotho, Madagascar and South Africa. Further initiatives in the region include the SwitchMed programme, Switch to Circular and the Promotion of Best Available Techniques (BAT) and Best Environmental Practices (BEP) to reduce u-POPs Releases from Waste Open Burning in Lesotho, among others.
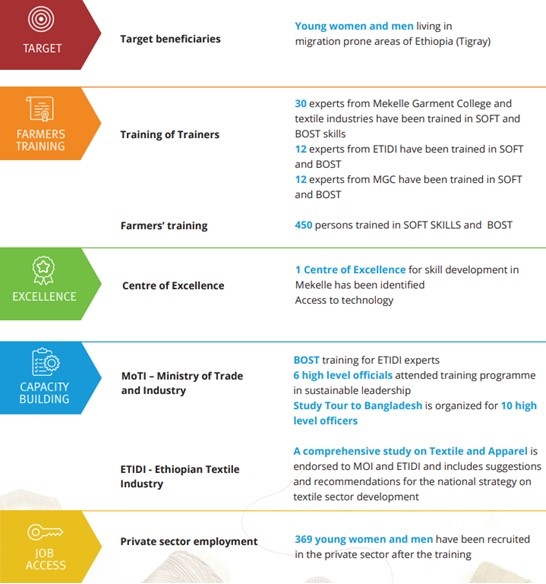
UNIDO contributes to related platforms and initiatives – to enhance synergies globally and ensure and promote gender equality and the empowerment of women. To help create decent and productive job opportunities for youth and women in the sector, UNIDO with the fund for the Italian Agency for Development Cooperation (AICS) developed the “Capacity-building and job creation for youth and women in the textile sector in migration prone areas of Ethiopia”, the target beneficiaries of this project are the young women and men living in migration prone areas of Ethiopia. See this table for the project interventions preliminary results:
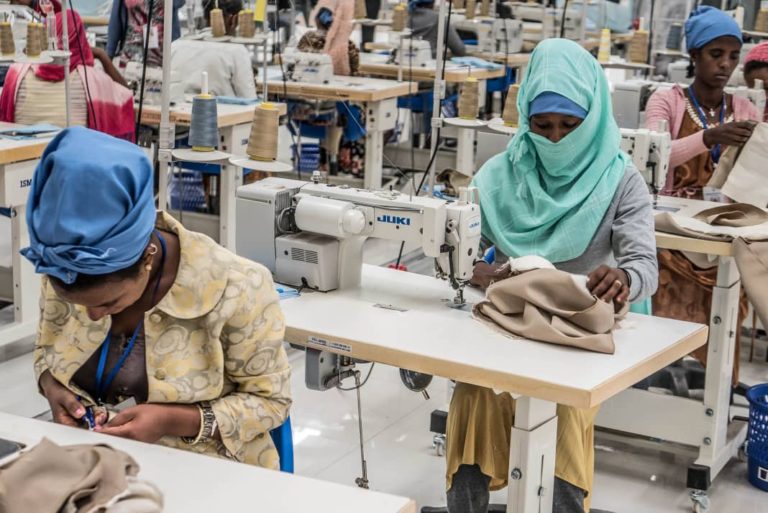

A wide range of activities are developed along the entire Fashion value chain under the Promotion of Circular Economy in the Textile and Garment Sector projects, including:
Under the EU-funded SwitchMed Programme, UNIDO undertakes actions in Egypt, Morocco and Tunisia that can develop the value chain of the textile and clothing industry to become more circular and less polluting. Together with global brands, international key experts, and local stakeholders, UNIDO develops an infrastructure to valorize pre-consumer textile waste and establish local capacities to help eliminate hazardous chemicals in textile and clothing production. Together with leading international brands, local industry stakeholders and the government, UNIDO strengthens local capacities to facilitate proper classification, efficient collection, sorting and recycling of post-industrial and pre-consumer textiles in line with global market specifications. To remove hazardous chemicals in the textile supply chain and reduce the large quantities of water required to manufacture fabrics, UNIDO is cooperating with the ZDHC Foundation, international brands, and local stakeholders to level up the local capacities to ensure systemic compliance with leading chemical protocols.
UNIDO’s Department of Agri-Business (Agro-Industries and Skills Development Division) has developed a Sustainable Textile and Garment Development Approach with five pillar strategies, including Innovation, Green, Fashionable, Digitalization and Inclusiveness strategies. The approach will cover a three modular approach and three cross-cutting services to contribute to the sustainable development of the fashion textiles industry. This approach focuses on the value chain suitability from fiber to garment, the Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) performance of textile investment and operation, the WE2CT Management of the value chain and the life cycle analysis of the product. As well as helping to generate employment and incomes, this approach also contributes to climate change and biodiversity efforts by supporting the development of a circular agribusiness that replaces chemicals with natural products, recreates value from left overs and waste, uses renewable energy, and regenerates natural ecosystems.
UNIDO’s Department of Energy supports the Sustainable Fashion approaches on Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation and on reducing the industry’s Green House Gas emissions. In particular, the Global Cleantech Innovation Programme (GCIP) and PFAN Programme support the Circular Economy in the Textile and Garment Sector projects to develop business models and financing mechanisms for the sustainability of waste recycling and reuse operations. They will also provide support on entrepreneurship development and business to business (B2B) linkages through their network of advisors in the region.
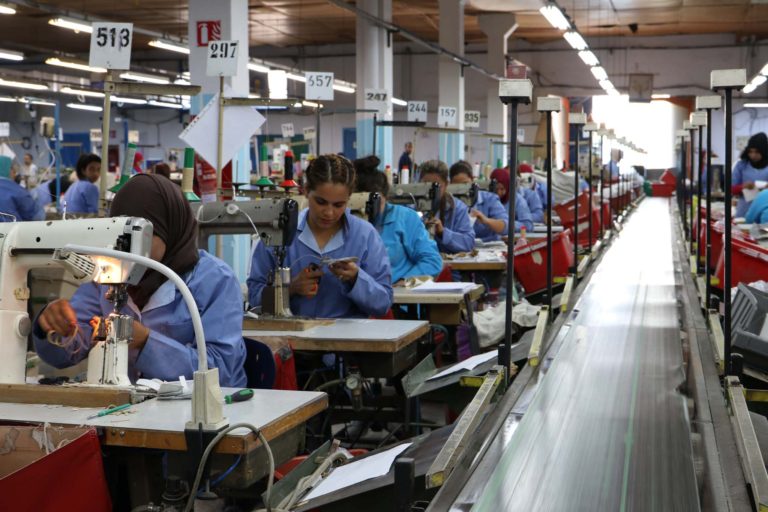
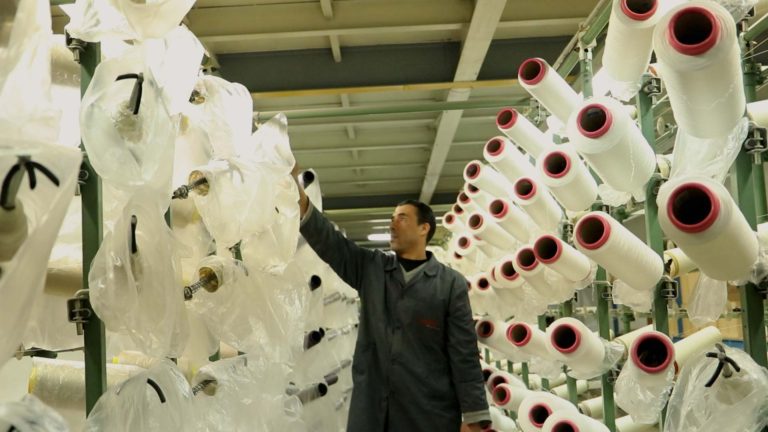


UNIDO has developed industry partnerships with a range of international brands, who are attracted to adopting a value chain approach to make their operations more sustainable. Furthermore, UNIDO sustainable fashion interventions engage various international partners and projects, including:
Receive news on the Alliance, upcoming events, and members activities in Sustainable Fashion
